Position of kidneys: Lie on the posterior wall of abdomen, outside the peritoneal cavity (space within abdomen lined by peritoneum, a type of serous membrane i.e. a serum secreting membrane).
Weight of each kidney: approx. 150 gm
Size of each kidney: approx. size of a clenched fist; 4-5 inches long, 2-3 inches wide, 1 inch thickness.
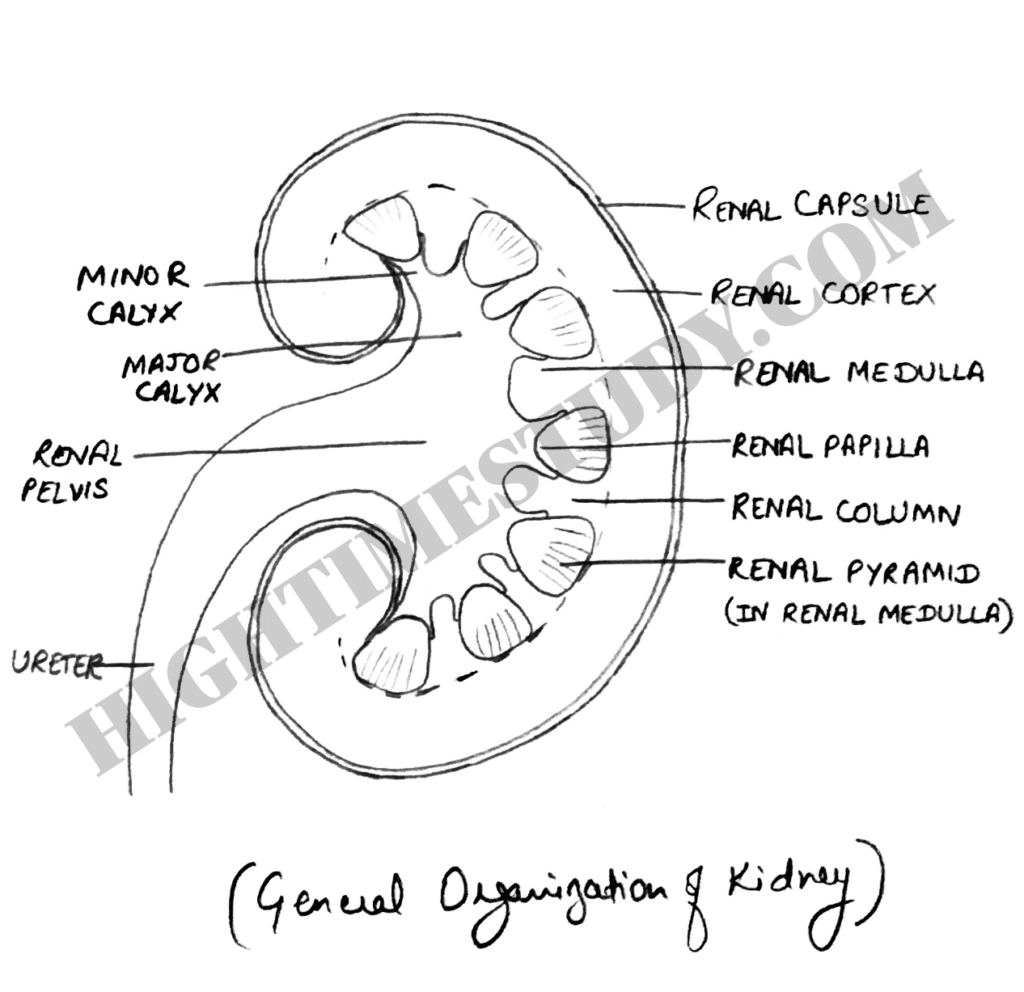
Hilum: The medial side of each kidney contains an indented region called hilum, which expands into renal sinus. Through hilum following structures pass through –
- Renal artery
- Renal vein
- Lymphatics
- Nerve supply
- Ureter
The above structures are protected and stabilized at their respective positions by adipose tissue/fat cells present in the renal sinus. Excess of fat in renal sinus may cause kidney damages.
Ureter: Muscular tube that carries urine from kidneys to urinary bladder.
Urinary Bladder: Muscular sac like structure that stores urine until emptied.
Urethra: Muscular duct from urinary bladder to the exterior of the body. In females, it conveys urine but in males, it conveys urine as well as semen.
Capsule of kidney: The kidney is surrounded by a tough, fibrous capsule which protect its delicate inner structure.
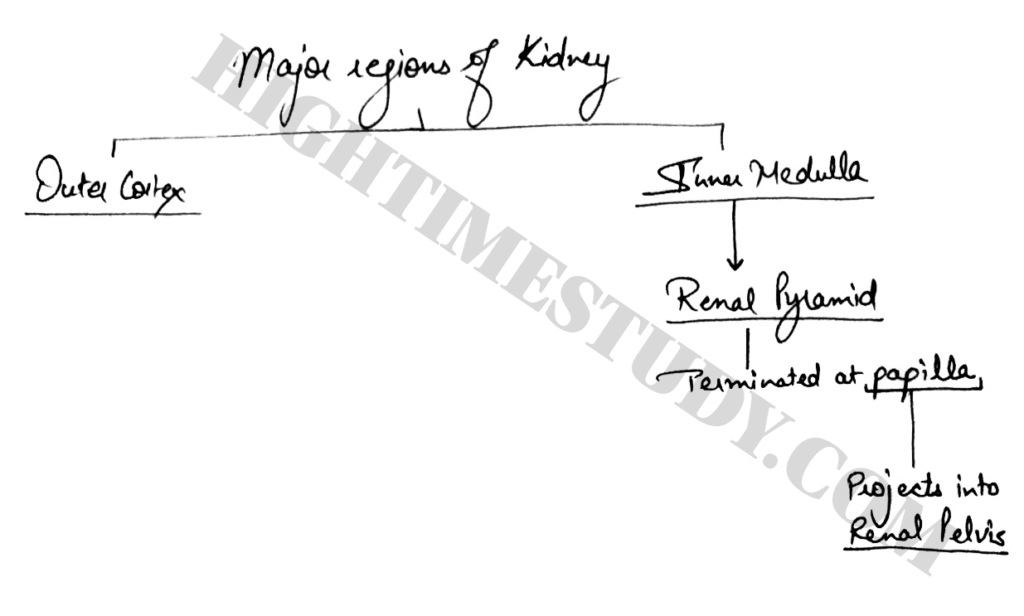
Major regions of Kidney
- Outer Cortex (Renal Cortex)
- Inner Medulla (Renal Medulla)
Inner Medulla
1) Inner medulla is divided into 8-10 cone shaped tissue masses called renal pyramids.
2) Each renal pyramid has its base origin at border between renal cortex and medulla and terminates in renal papilla.
3) Each renal papilla projects into a space called renal pelvis.
4) Renal pelvis is a funnel shaped continuation of upper end of ureter.
5) Major calyx (pl. calyces): Outer border of the renal pelvis is divided into pouches (open ended) known as major calyces.
6) Minor calyx (pl. calyces): Major calyx extends further and divides into minor calyces which collect urine from tubules of papilla.

The walls of calcyes, pelvis and ureter contain contractile elements enabling the movement of urine towards bladder.
Renal Parenchyma = Renal Cortex + Renal Pyramids
